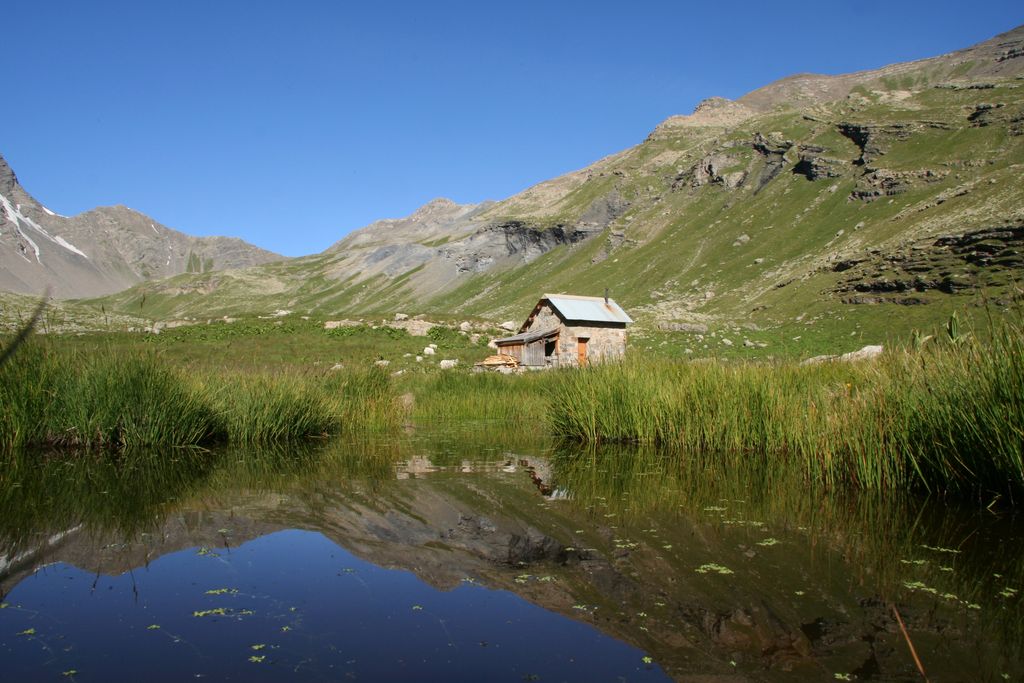

The Grande Cabane
« At sunrise, as I went up to carry out a sanitary check on the chamois goats in Clouzis valley, the grass suddenly moved under my shoes. It was a slow worm, this lizard without legs which is very rare to see at altitude. »
Jean-Philippe Telmon, park ranger in Vallouise.
Description
From the carpark at Deslioures, take the path on the right, the alternative itinerary on the GR54 (Tour de l'Oisans).
- Go along several bends in « la Folie » to reach the plateau which will take you along a gentle elevation, by the « Malafosse » shale, to the pastoral cabin of Balme.
- Continue on the elevated path under the cabin until the torrent at Clausis, the entrance into the heart of the national park, then up to the Grande Cabane, positioned above the glacial cross cliff at Fournel.
- Go down by the same track. It is possible to continue towards the Pas de la Cavale, mountain pass which enables you to get back to the Pré de la Chaumette in the Champsaur.
- Departure : La Salce, l'Argentière-la-Bessée
- Towns crossed : L'Argentière-la-Bessée
Altimetric profile
Recommandations
The carpark is two steps away from the Deslioures nature reserve, the biggest European site for The Queen of the Alps (Alpine Sea Holly), a protected plant. It usually flowers at the end of June and the beginning of August. It is forbidden to pick this plant.
 In mountain pastures, protection dogs are there to protect the herds from predators (wolves, etc.).
In mountain pastures, protection dogs are there to protect the herds from predators (wolves, etc.).
When I hike I adapt my behavior by going around the herd and pausing for the dog to identify me.
Find out more about the actions to adopt with the article "Protection dogs: a context and actions to adopt".
Tell us about your meeting by answering this survey.
Information desks
Vallouise Park house
, 05290 Vallouise
Information, documentation, models, exhibitions, screenings, product sales and works of the Park. Guided tours for school, reservation required. The new Park House opened in Vallouise since June 1, and offers visitors an interactive permanent exhibition inviting to explore the area and its heritage. A temporary exhibition space will allow a renewed offer. Finally, the device is completed by an audiovisual room to organize screenings and conferences Free admission. All animations of the Park are free unless otherwise stated.
Access and parking
In Argentière-la-Bessée, follow the direction Vallon du Fournel. NB. Road usually closed in winter, 200 m after the hamlet at l'Eychaillon (1250 m).
22 points of interest

Coronelle lisse - Damien Combrisson - PNE  Fauna
FaunaSmooth snake
In the first bends of the path, the big slates heat up under the sun. Sometimes, one of them becomes the hideout of a small snake, the smooth snake. Everything about it is soft: its rounded lines, its smooth scales, its round pupils, its pink grey colour. A dark band around its muzzle, passes under the eye and goes round behind the head, forming the crown which gives it its name in French. Discreet and inoffensive, it hunts lizards sunning themselves and who hide at the slightest sound.

Démonstration de débitage des ardoises à l'ardoisière de de la Salce - Yves Baret - PNE  Geology and geography
Geology and geographyThe old slate quarry
Between 1851 and 1953, a slate quarry in the Salce was intermittently exploited. The slate was used for the rooves of houses. Its weight (40 kg au m²) ensured that the wind could not blow it away. The slate, presented an enormous advantage over thatch: in that there was no risk from fire. Blocks were cut in winter and in consequence this activity was complementary to the agricultural work.

Fruits du genévrier commun - Jean-Pierre Nicollet - PNE  Flora
FloraCommon Juniper
Able to live up to 400 years, this shrub looks hunched over and can even creep along when it has reached its altitudinal limit. Lower down, it adopts a rigid princely position. Its needles are very sharp and are positioned in threes. Its violet fleshy fruit is only carried by the female parts of the plant enabling them to be correctly identified. They are used as aromatics for their digestive properties. The inhabitants of the Briançon vallies chew the berries to protect against « cold snaps » and at Freissinières, the vapour of the juniper is recommended against colds.

Cigalette à ailes courtes - Damien Combrisson - PNE  Fauna
FaunaThe short winged small cicada
This small cicada is quite common on the warm dry side of the valley. To see it, it is best to be patient! But it is child’s play to hear its very high sound with a low intensity. It is a buzzing crescendo followed by a brief separated accent: « Tsssssssssss... tsit ». The larva lives for a few years in the ground, then on a hot day it jumps onto a branch to transform itself in to a flying and singing insect to attract males. Sometimes, you can find a discarded exoskeleton under a juniper bush, the envelope left by the larva after moulting.

Digitales à grandes fleurs - Jean-Philippe Telmon - PNE  Flora
FloraLarge flowered foxglove
This large flower does not go unnoticed with its bunch of yellow corolla. Its name in French ‘digitale’ comes from its similarity to the thimble in which one slips ones finger. In common parlance, its name is « witch’s glove » because it is a highly poisonous plant.

Violette à éperon, ou pensée des Alpes - Cédric Dentant - PNE  Flora
FloraThe mountain violet
As a carpet of violet flowers, sometimes yellow, white or mixed, the mountain violet adorns fresh grass with its colours. We call it the spurred violet. In fact its spur is visible on the back of the flower,it is long and only insects with a long tongue like the butterflies can collect pollen from them. Violets and pansies are part of the same family. To tell them apart, you just have to look at the two lateral petals: oriented downwards for violets and upwards for the pansies. The pansy is an optimistic flower!

La cabane de la Balme - Thierry Maillet - PNE  Pastoralism
PastoralismThe cabin of the Balme
The cabin of the Balme is situated on the plateau of the same name, a little above the path. This site offers an uninterrupted view of the bottom of the Fournel valley and its steep summits. This cabin, like the one at Salce and the Grande Cabane, is used for the shepherds work. Please respect its tranquility.

Grande fétuque - Manuel Meester  Flora
FloraEast alpine violet fescue
The East alpine violet fescue is an early perennial grass, it grows in tufts and can have up to 50 leaves, which are between 30 to 50 cm long. They thicken and harden with maturity and become increasingly less appetizing for animals grazing late in the season. In this way the East alpine violet fescue spreads, forming large patches in the alpine meadow: called “le queyrellin” On the sunny side of the Fournel valley, agri-environmental measures envisage adapted grazing in order to limit the extension of the East alpine violet fescue in order to preserve the floral diversity of the alpine meadow.

Faucon crécerelle en vol - Mireille Coulon - PNE  Fauna
FaunaThe common kestrel
A small, elegant bird of prey with a red back, black wing tip flies away. Above the prairie, it is immobile in the position of the « Holy spirit », The tail fanned out, before diving down to its prey. It is a common kestrel, the most frequently seen falcon. Also called « speckled » because of its speckled feathers, it is easy to observe it above the pastures heated by the sun.

Plissement géologique dans le Fournel - Thierry Maillet - PNE  Geology and geography
Geology and geographySteep sandstone ditches in the Champsaur
On the steep slopes of the summits which border the Fournel valley there are a multitude of folds whose ridges follow a repetitive theme. It is the most visible sign of an intense global shearing of the surface.

Troupeau dans le vallon du Fournel - Jean-Philippe Telmon - PNE  Pastoralism
PastoralismPasture and flocks
A large flock of sheep bringing together several flocks from the community of L'Argentière-la-Bessée grazes in the Fournel valley during the hot weather. The shepherd brings the sheep up during the summer and takes them back down again at the end of the pasture to eat the second crop of Queen of the Alps which have planted their seeds. During the grazing the shepherd, uses three cabins: the one at Salce, the one at Balme and the Grande Cabane.

Monticole de roche - Pascal Saulay - PNE  Fauna
FaunaCommon Rock Thrush
On a crag of rock, orange breast, blue head and white rump, a bird flies away making a melodious, sweet and clear song. The Common Rock Thrush does not only live in the mountains but prefers stones and sunshine above everything else. As soon as it returns from its migration at the end of April, it searches for a place to reproduce and it makes its presence known. Inspite of its bright colours, this bird knows how to be discreet and you will be lucky to observe it on a rock near to the Grande Cabane.

Traquet motteux - Damien Combrisson - PNE  Fauna
FaunaWheatear
At the end of April, on the soil of the pasture, the snow melts progressively. The rocks are used as perches by the Wheatear, who has just returned from its migration. The male appears first: in breeding plumage, he has a grey head and back, a mask like Zorro over the eyes, a white abdomen and dark wings. He is easily recognized in flight by his white rump and the black T shape made by his tail. The female is paler and less contrasted. Often positioned on a jutting rock , they watch their surroundings looking for insects.

Champ d'asphodèles - Pascal Saulay - PNE  Flora
FloraWhite Asphodel
The White Asphodel is a plant that is big in size, visible from a distance, it appreciates chalky soils. Its white flowers blossom in time along the floral spike situated at the end of a thick stem. . This is why we can observe fruit at the bottom of the spike even though the flowers at the top of the spike are still in bud. Its long narrow leaves are grouped at the base of the stem, they give it it’s common name « the dogs’ leek ».

Vipère aspic - Damien Combrisson - PNE  Fauna
FaunaThe aspic viper
Taken by surprise whilst basking in the sun, a snake suddenly weaves its way into the grass just in front of the walker's step foot. With its triangular head, vertical pupil, stocky body, short tail and quite a snubbed nose, this is an aspic viper. Instinctively the walker flees. However, the snake has long since disappeared into its hole. Snakebites are extremely rare as the viper only attacks in defence if it is caught or if it is stepped on. It would much rather keeps its venom for small rodents, lizards or sparrows which are swallowed whole, then slowly digested.
Rubanier à feuilles étroites - Cédric Dentant - PNE  Flora
FloraNarrow leaf bur-reed
It is in the calm shallow water of the small lake facing the Grande Cabane that a dense colony, of narrow leaf bur-reed has developed. Its leaves, flat and long, float on the surface of the water while its flowers rise above the surface of the water. Starting off as green balls with spiky points, they blossom into yellow balls, spreading their pollen to the four winds. Formerly harvested, the « water ribbons » were used as ties, fodder or padding.

La grande cabane, vallon du Fournel - Cyril Coursier - PNE  Pastoralism
PastoralismThe Grande Cabane
The point of the hike, the Grande Cabane seems lost in the immensity of the high Fourne valley. This cabin is used by the shepherd. A shelter for hikers is available in the old cabin situated against the rocky escarpment, on the other shore of the torrent. This pasture is part of the network of « Sentinel Pastures », a system that studies the different physical, natural and human parameters in order to understand and anticipate the impact of climate change on the pastures in the Ecrins and the Alpes. Covered with ancient moraines, the terrain is softened, the landscape less harsh. On this lower shelf, the Fournel meanders calmly and you can observe small lakes and wetland .Several indications of the presence of ancient human life have been discovered here by archeologists, the oldest going back to prehistoric times.

Le vallon du Fournel vu depuis la Salce - Marie-Geneviève Nicolas - PNE  Geology and geography
Geology and geographyThe Fournel « boutonnière »
From the Deslioures carpark, you can observe the Fournel running into the canyons of the Balme, carved out in the crystalline base covered wih Champsaur sandstone. There the erosion has slowly, smoothed the sandstone covering, to slash the crystalline rocks over 300 m. It is the Fournel “boutonnière”. On the path, it is easy to see the junction between the crystalline rocks and their sandstone covering separated by a thin intermediary layer of Limestone with a rim form, commonly called the Balme, which gives its name to the pasture and to the cabin.

Cabane de la Balme et Pic Félix - Jean-Philippe Telmon - PNE  Top
TopThe Pointe des Rougnoux and Pic Félix
The Pointe des Rougnoux (3179 m) is an easily recognizable summit because it is composed of several peaks and is shared between the vallies of Champoléon in Champsaur, Fournel and Freissinières on the Durance side. The Pic Félix Neff (3243 m) has a north slope towards the Fournel valley and its south slope above the hamlet of Dormillouse where the pastor Félix Neff was established in 1823. A real « apostle of the Hautes-Alpes », this pastor from Geneva worked as an evangelist, teacher, agronomist and engineer. At Dormillouse, he preached and improved daily life (he cultivated potatoes, created irrigation channels, and improved the sanitation in the stables).

Abri randonneur GR541 - Blandine Delenatte - PNE  Architecture
ArchitectureWalker's shelter
Opposite the Grande Cabane, a sign indicates: "GR54 shelter". Indeed, perched on the rocky ledge is a simple, damp, stone shelter that provides a roof for walkers on the GR route in the case of bad weather. It has not yet been restored, and offers little more for the time being.
Crave à bec rouge en vol - Mireille Coulon - PNE  Fauna
FaunaRed billed Chough
A flying companion to the yellow billed Chough, the red billed Chough plays in the clouds and breaks the silence with its brief strident cry, which sounds almost metallic .Alerted by the echo coming from the canyon wall, it is joined by its companions stride meticulously on foot across the pasture to extract the grass crickets and small worms. Their legs are as red as their beak and we most often see them in the sky flying in a couple.

Vol de chocards à bec jaune - Mireille Coulon - PNE  Fauna
FaunaYellow billed Chough
A whirl of black birds moves noisily along the edge of the Fournel before landing amongst the juniper bushes. In a joyful rumpus, they come to feed on the blue berries that winter has left them. In the air they make breathtaking, demonstrations of flying in formation like a school of fish in the ocean. .The yellow billed Chough is friendly and will not hesitate to approach hikers in order to peck the crumbs from their picnics.
Source

Report a problem or an error
If you have found an error on this page or if you have noticed any problems during your hike, please report them to us here:


